Auto in Spain
Team Leader: Cynthia Yi
Analysts: Mohammed Rajpar, Nur Al-Ebeid, Michael Juranka, Matthew Gordin, and Bita Pejam.
The Kingdom of Spain is located in Southwestern Europe, bordered by Portugal and France with its coastline along the Mediterranean Sea.[i] Spain is ranked as the 15th largest export economies in the world, making it a vital contributor to the international community.[ii]
Current Political Situation
Spain is a parliamentary constitutional monarchy with a bicameral legislative system. Since June 2014, King Felip VI has reigned as the Chief of State. [iii] The current Prime Minister of Spain is Pedro Sanchez of the Socialist Workers Party (Partido Socialista Obrero Español: PSOE). Sanchez was elected after the previous leader, Mariano Rajoy was forced to step down due to the vote of no-confidence in June 2018, stemming from corruption scandals within the opposition party, the Popular Party (PP). Political instability may also be expected with the fact that the PSOE is ruling with a minority government, holding 84 out of 350 seats in the lower chamber of parliament. This outcome was also after multiple elections were held to confirm clear support for the ruling party.[iv]
The country is divided into 17 autonomous communities and 2 autonomous cities which leads to complexity in the regulatory system across the different regions. [v] The country’s division holds implications regarding territorial issues such as the secessionist movements that have stemmed from the differences between communities. Investors should be aware of the internal conflicts as they bring with them risks such as escalating riots in Catalonia and possible Islamist terrorist attacks.
Economic Size-Up
Spain, a member of the European Union since 1986, is one of the world’s largest economy placed fourteenth with a nominal GDP of $1,311,320.02 USD.[vi] Spain’s economy has been characterized by a high unemployment rate, especially unemployment of youth. This can be attributed to the 2008 recession, which resulted in the unemployment of 26% in 2013[vii]. Another contributing factor towards the labour concerns is shown by the 2014 report from the OECD which notes that Spain ranks far below the OECD average in education rates[viii]. Currently, Spain has a labour force participation rate of 75.1%[ix], an unemployment rate of 15.2%[x], and a youth unemployment rate of 38.7%[xi]. Spain’s Unemployment Rate 2008 - 2018: Unemployment peaked at the end of 2013, a result of the 2008 Financial Crisis, and the subsequent European Debt Crisis. Although it has since improved, it remains far higher than pre-recession lows, largely driven by high youth unemployment, as seen in Figure 1. High unemployment will maintain steady and low inflation for the near future, but will also result in significant economic slack.[xii] Broadly speaking, the economic outlook for Spain is bright, as the OECD expects it to continue growing (albeit at a moderate pace) over the next two years.[xiii] However, European Commission forecasts that Spain’s GDP growth will slow over the next 3 years.
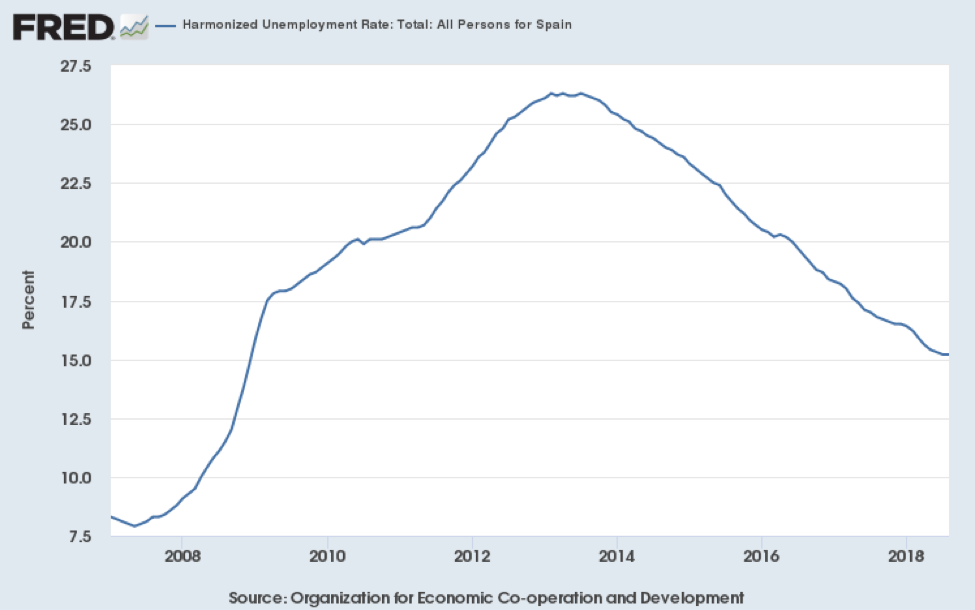
Figure 1
Automotive Industry Overview
Automobiles are the top exported goods in Spain, in 2017 the automotive industry produced $57 USD, which accounted for the highest percentage of total exports. The leading passenger car brands by market share are as follows: Renault Espana (8.18%), Seat (7.61%), Volkswagen (7.22%), Peugeot (7.07%), Opel (7%), Citroen (5.51%), Ford (5.5%), Toyota (5.34%), Nissan (5.03%), Dacia (3.74%).[xiv]
With regards to foreign investment, the auto industry in Spain is the second largest recipient of German investment. In 2015 the total German investment received was €4.8 billion, of which €4 billion was specifically for the auto industry.[xv] Growth in the auto industry has been consistent since it recuperated after the credit crash with an annual growth of around 5-10% every year since 2012 (45% between 2012-16).[xvi] Future issues facing the export of automotive may be from currency devaluations and protectionist policies in Europe, as the United Kingdom is one of the biggest markets for Spanish vehicles.[xvii] Possible risks specific to UK-Spanish relations is the Brexit agreement, reached in 2017, and contention over Gibraltar. From 2011 onwards, Spain became the number one foreign direct investment destination for the automotive industry in Europe even when compared to the central and eastern European countries.[xviii]
Executive Summary
In addition to the aforementioned risks, with the automotive sector being one of the key industries in the Spanish economy, there is a large government presence in the industry. Thus, risks stemming from government intervention is also high as new regulations may be imposed to adjust to new governmental priorities. These should all be taken into consideration as it will affect future and current investors in the market. The risks that our team will be exploring include the economic, political, regulatory, international, and labour risks regarding the automotive industry in Spain.
[i] “The World Factbook: Spain.” Central Intelligence Agency https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/geos/sp.html
[ii] “Spain.” OEC. https://atlas.media.mit.edu/en/profile/country/esp/
[iii] “The World Factbook: Spain.” Central Intelligence Agency https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/geos/sp.html
[iv] “Spain Country Report.” Garda World. https://www.garda.com/crisis24/country-reports/spain
[v] “The World Factbook: Spain.” Central Intelligence Agency. https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/geos/sp.html
[vi] "GDP (current US$)." World Bank. https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/NY.GDP.MKTP.CD?year_high_desc=true.
[vii] Central Intelligence Agency. (2018). CIA World Factbook - Spain. [online] Available at: https://www.cia.gov/llibrary/publications/the-world-factbook/geos/sp.html
[viii] "Spain Country Note: Education at A Glance". 2014. OECD. http://www.oecd.org/education/Spain-EAG2014-Country-Note.pdf
[ix] "OECD DATA: Employment - Labour Force Participation Rate". 2018. OECD. https://data.oecd.org/emp/labour-force-participation-rate.htm.
[x] "OECD Harmonized Unemployment Rate: Total: All Persons For Spain". 2018. FRED - St. Louis Federal Reserve. https://fred.stlouisfed.org/graph/?id=LRHUTTTTESM156S,LRUN64TTESQ156S,LMUNRLTTESM647S.
[xi] "OECD DATA: Unemployment – Youth unemployment rate". 2018. OECD. https://data.oecd.org/unemp/youth-unemployment-rate.htm.
[xii] "2018 Global Economic Outlook". 2018. Goldman Sachs. https://www.goldmansachs.com/insights/pages/2018-global-economic-outlook-as-good-as-it-gets.html.
[xiii] "OECD: Spain - Economic Forecast Summary (May 2018)". 2018. OECD. http://www.oecd.org/eco/outlook/spain-economic-forecast-summary.htm.
[xiv] “Market share of leading passenger car brands in Spain in 2017.” 2017. Statista. https://www.statista.com/statistics/417410/leading-car-brand-sales-in-spain/
[xv] Mendez-Barreira, Victor. “Car Makers Pour Money Into Spain.” 2016. Wall Street journal. https://www.wsj.com/articles/car-makers-pour-money-into-spain-1470613487
[xvi] “Market Monitor Automotive Spain.” 2017. Atradius. https://atradius.nl/rapport/market-monitor-automotive-spain-2017.html
[xvii] “Spain's car industry is back on track (but could be derailed by Brexit).” 2017. The Local Europe. https://www.thelocal.es/20170118/spains-automobile-industry-is-back-on-track-but-could-be-derailed-by-brexit
[xviii] “Foreign direct investment in the automotive sector set to trap CEE countries and Spain in low-wage competition.” 2017. European Trade Union Institute. https://www.etui.org/News/Foreign-direct-investment-in-the-automotive-sector-set-to-trap-CEE-countries-and-Spain-in-low-wage-competition

